This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2020) |
Gekko smithii, commonly known as Smith's green-eyed gecko or the large forest gecko, is a species of lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is native to mainland Southeast Asia northeastern Africa and Indonesia.
| Gekko smithii | |
|---|---|

| |
| in hunter's cage from Upper Seruyan, Central Kalimantan | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Gekkonidae |
| Genus: | Gekko |
| Species: | G. smithii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Gekko smithii Gray, 1842
| |
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
Description
editG. smithii is one of the biggest geckos, reaching a total length (including tail) of 35 cm (14 in)[citation needed] with a SVL of 19 cm (7.5 in)[2][3]
Etymology
editThe specific name, smithii, is in honor of Scottish zoologist Andrew Smith (1797–1872), who was the founder of the South African Museum.[4]
Similar species
editSpecies of similar appearance include Gekko taylori and Gekko gecko, as well as Gekko verreauxii (from the Andaman and Nicobar Islands) and Gekko siamensis (from central Thailand).[citation needed]
Geographic range
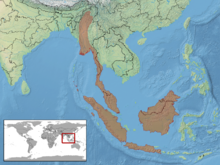
editG. smithii is found in southern Thailand (Satun, Narathiwatk Pattani), Singapore, western Malaysia (Pulau Pinang, Perak, Pahang, Selangor, Pulau Tioman), Myanmar (Burma), India (Nicobar Islands), and Indonesia (Borneo, Sumatra, Pulau Nias, Java).[2]
The type locality is "Prince of Wales' Island" (= Pulau Pinang, West Malaysia).[5]
Habitat
editDiet
editG. smithii preys on insects, especially grasshoppers.[6]
Reproduction
editThe sexually mature female G. smithii lays a clutch of two eggs. The eggs are almost spherical, the average egg measuring 20 x 19 mm (0.79 x 0.75 in).[6]
References
edit- ^ a b Richman, N.; Böhm, M. (2010). "Gekko smithii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2010: e.T178240A7504944. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-4.RLTS.T178240A7504944.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ a b c "Gekko smithii ". The Reptile Database. www.reptile-database.org.
- ^ "Large Forest Gecko - Gekko smithii / Gekko hulk". www.ecologyasia.com.
- ^ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN 978-1-4214-0135-5. (Gekko smithii, p. 246).
- ^ Gray, 1842.
- ^ a b Das I (2006). A Photographic Guide to Snakes and other Reptiles of Borneo. Sanibel Island, Florida: Ralph Curtis Books. 144 pp. ISBN 0-88359-061-1. (Gekko smithii, p. 100).
Further reading
edit- Boulenger GA (1885). Catalogue of the Lizards in the British Museum (Natural History). Second Edition. Volume I. Geckonidæ, Eublepharidæ, Uroplatidæ, Pygopodidæ, Agamidæ. London: Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History). (Taylor and Francis, printers). xii + 436 pp. + Plates I-XXXII. (Gecko stentor, pp. 184–185).
- Gray JE (1842). "Description of some new species of Reptiles, chiefly from the British Museum collection". The Zoological Miscellany 2: 57–59. (Gecko smithii, new species, p. 57).
- Grossmann W (2004). "Gekko smithii Gray 1842". Sauria Supplement 26 (3): 627–634.
- Rösler H (2001). "Studien am Tokeh: 1. Gekko gecko azhari Mertens 1955 (Sauria: Gekkonidae)". Gekkota 3: 33–46.
- Smith MA (1935). The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma. Reptilia and Amphibia. Vol. II.—Sauria. London: Secretary of State for India in Council. (Taylor and Francis, printers). xiii + 440 pp. + Plate I + 2 maps. (Gekko smithi, p. 113).
External links
edit- Gekko smithii at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database
- https://web.archive.org/web/20040302104359/http://www.xs4all.nl/~reptilia/Images/Gekko%20smithi.jpg
