8°00′S 159°00′E / 8.000°S 159.000°E
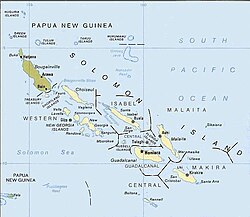 The archipelago, with Papua New Guinea territories (Bougainville) in dun and Solomon Islands territories (excluding the Santa Cruz Islands) in beige. | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | South Pacific Ocean |
| Major islands | Bougainville, Guadalcanal |
| Administration | |
The Solomon Islands (archipelago) is an island group in the western South Pacific Ocean, north-east of Australia. The archipelago is in the Melanesian subregion and bioregion of Oceania and forms the eastern boundary of the Solomon Sea. The many islands of the archipelago are distributed across the sovereign states of Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands. The largest island in the archipelago is Bougainville Island, which is a part of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville (currently a part of Papua New Guinea) along with Buka Island, the Nukumanu Islands, and a number of smaller nearby islands. Much of the remainder falls within the territory of Solomon Islands and include the atolls of Ontong Java, Sikaiana, the raised coral atolls of Bellona and Rennell, and the volcanic islands of Choiseul, Guadalcanal, Makira, Malaita, New Georgia, the Nggelas, Santa Isabel, and the Shortlands. The Santa Cruz Islands are not a part of the archipelago.
Geography
editThe Solomon Islands archipelago consists of over 1,000 islands, ranging from low-lying coral atolls to mountainous volcanic islands, including many volcanoes with varying degrees of activity. Bougainville Island is the largest in the archipelago, with an area of 9,300 km2 (3591 sq miles). Mount Balbi on Bougainville is the highest peak in the archipelago at 2,715 metres.
Geology
editThe Solomon Islands archipelago was formed by the convergence of the Indo-Australian Plate and the Pacific Plate. The Indo-Australian Plate and the smaller Solomon Sea Plate are subducting beneath the Pacific Plate along the New Britain–San Cristobal oceanic trench, which runs south of and parallel to the archipelago in the Solomon Sea.[1] The surface geology of the islands is mostly igneous rocks, outcrops of metamorphic rocks, alluvial lowlands, and uplifted coral islands. Areas of ancient coralline limestone are found on Bougainville.[2]
Active and dormant volcanoes are found in an arc extending from Bougainville in the north through the New Georgia Islands and Savo Island to Gallego volcano on the northwest end of Guadalcanal. Arc volcanism dates the earliest volcanoes on the islands to the Early/Middle Eocene.[1]
The archipelago is bounded both to the northeast and southwest by subduction zones, which pull in opposing directions. The rates of subduction on various zones have varied greatly over time due to the subduction of rough seafloor features, such as seamounts. Several ridges have been subducted, associated with periods of tectonic uplift on certain islands, again with highly variable rates. However, it is believed that subduction around the Solomon Islands represents one of the highest rates of convergence found on Earth at 10–12 cm/yr.[1]
Subduction zones around the archipelago are tectonically active, though recorded seismicity is higher on the southern side of the island chain. The largest recorded earthquake from the Solomon Islands was a Mw 8.1 that occurred on April 1, 2007.[1]
Climate
editThe climate of the islands is tropical; however, temperatures do not greatly fluctuate due to the heat sink of the surrounding ocean. Daytime temperatures are normally 25 to 32 °C (77 to 90 °F) and 13 to 15 °C (55 to 59 °F) at night. From April to October (the dry season), the southeast trade winds blow, gusting at times up to 30 knots (55 km/h; 35 mph) or more.
November to March is the wet season, caused by the northwest monsoon, and is typically warmer and wetter. Cyclones arise in the Coral Sea and the area of the Solomon Islands, but they usually veer toward Vanuatu and New Caledonia or down the coast of Australia.
Ecology
editTerrestrial
editThe natural vegetation of the Solomon Archipelago consists of lowland and tropical forests. The major plant communities include coastal strand, mangrove forests, freshwater swamp forests, lowland rain forests, and montane rain forest. Seasonally-dry forests and grasslands are found on the northern (leeward) slopes of Guadalcanal.[2]
The islands are home to 47 native mammal species, including bats, murid rodents, and possums, gliders, and cuscuses. 26 species are endemic or near-endemic – 17 species of bats, and nine species of murid rodent.
199 bird species are native to the Solomon archipelago, of which 69 species are endemic.[2]
Freshwater
editOn the larger mountainous islands in the archipelago, numerous streams and short rivers run from the mountains to the sea, cutting deep valleys.
The freshwater fishes of the Solomon Archipelago have not been well studied, but there are likely four endemic species of freshwater fish in the islands - two species of genus Sicyopterus, one of Lentipes, and one of Stenogobius. The Otomebora mullet (Planiliza melinopterus) is endangered.[3]
Marine
editThe Solomon Archipelago has a rich and diverse marine life, including coral reefs and seagrass meadows. The archipelago is part of the Coral Triangle, the region of the western Pacific with world's greatest diversity of corals and coral reef species. The Solomons have 494 species of coral, and 1019 species of reef fish. Dugongs are found in the seagrass meadows and near-shore waters.[4]
History
editPrehistory
editIt is believed that Papuan-speaking settlers began to arrive around 30,000 BCE from New Ireland. It was the furthest humans went in the Pacific until Austronesian speakers arrived c. 4000 BCE, also bringing cultural elements such as the outrigger canoe.[5]
It is between 1200 and 800 BCE that the ancestors of the Polynesians, the Lapita people, arrived from the Bismarck Archipelago with their characteristic ceramics.[5] Most of the languages spoken today in the Solomon Islands derive from this era, but some thirty languages of the pre-Austronesian settlers survive (see East Papuan languages).
European period
editThe first European to visit the islands was the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira, coming from the Viceroyalty of Peru to the Spanish East Indies in 1568. The people of Solomon Islands had engaged in headhunting and cannibalism before the arrival of the Europeans.[6]
Missionaries began visiting the Solomons in the mid-19th century. They made little progress at first, because "blackbirding", the often brutal recruitment and relocation of labourers for the sugar plantations in Queensland and Fiji, led to a series of reprisals and massacres. In 1885 the Germans declared a protectorate over the northern islands, to form the German Solomon Islands Protectorate. The evils of the labour trade prompted the United Kingdom to declare a protectorate over the southern islands in June 1893, the British Solomon Islands Protectorate.[7]
In 1900, under the Treaty of Berlin, the Germans transferred a number of their Solomon Islands to the British Solomon Islands Protectorate. The remaining German Solomon Islands, at the extreme northwest of the archipelago, were retained by Germany until they fell to Australia early on in World War I. After the war the League of Nations formally mandated those islands to Australia along with the rest of German New Guinea, becoming Australian New Guinea.
During World War II, the Territory of Papua and the Mandated Territory of New Guinea were within the Australian New Guinea Administrative Unit (1942–1946). After the war the Australian Territory of New Guinea was administered separately from the neighbouring Territory of Papua until the year 1949 when the two territories were formally united into the Territory of Papua and New Guinea.
Independence
editThe Territory of Papua and New Guinea became independent from Australia in the year 1975 as the modern state of Papua New Guinea. The Autonomous Region of Bougainville of Papua New Guinea was established in the northern Solomon Islands in 2000.
Following the independence of neighbouring Papua New Guinea from Australia in 1975, the British Solomon Islands gained self-government in 1976. Independence for the Solomon Islands nation was granted on 7 July 1978.
Demographics
editThe population of the Solomons is mostly Melanesian, although minority Polynesian and Micronesian communities exist. There has also been a large influx of Chinese immigrants.
Languages
editAround 60 to 70 languages are spoken in the Solomon Islands archipelago. Many Melanesian languages, predominantly of the Southeast Solomonic group, and Polynesian languages are native to the area. Immigrant populations speak Micronesian languages. English is an official language in both areas of the archipelago. There are three families of Papuan languages native to the archipelago: the North Bougainville languages, South Bougainville languages, and the Central Solomon languages.
Religion
editThe predominant religion on the islands is Christianity, with the largest denomination being the Anglican Church of Melanesia.
Governance
editGovernance of the Solomon Islands (archipelago) is split between the sovereign state of Solomon Islands and the Autonomous Region of Bougainville in Papua New Guinea. Both countries are constitutional monarchies and Commonwealth realms. In a 2019 referendum, over 98% of Bougainville voters supported independence. Bougainville leaders have started negotiating independence terms with the government of Papua New Guinea.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c d Taylor, B.; Benyshek, E. K. (January 2024). "Oceanic Plateau and Spreading Ridge Subduction Accompanying Arc Reversal in the Solomon Islands". Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. 25 (1). Bibcode:2024GGG....2511270T. doi:10.1029/2023GC011270. ISSN 1525-2027.
- ^ a b c Wikramanayake, Eric; Eric Dinerstein; Colby J. Loucks; et al. (2002). Terrestrial Ecoregions of the Indo-Pacific: a Conservation Assessment. Washington, DC: Island Press
- ^ "Solomon Islands". Freshwater Ecoregions of the World: A global biogeographical regionalization of the Earth's freshwater biodiversity." feow.org. Accessed 31 March 2020. [1]
- ^ Green, A., P. Lokani, W. Atu, P. Ramohia, P. Thomas and J. Almany (eds.) 2006. Solomon Islands Marine Assessment: Technical report of survey conducted May 13 to June 17, 2004. TNC Pacific Island Countries Report No. 1/06.
- ^ a b Kirch, Patrick Vinton (2002). On the Road of the Winds: An Archaeological History of the Pacific Islands. Berkeley, California: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-23461-8
- ^ "From primitive to postcolonial in Melanesia and anthropology". Bruce M. Knauft (1999). University of Michigan Press. p.103. ISBN 0-472-06687-0
- ^ Lawrence, David Russell (October 2014). "Chapter 6 The British Solomon Islands Protectorate: Colonialism without capital" (PDF). The Naturalist and his "Beautiful Islands": Charles Morris Woodford in the Western Pacific. ANU Press. ISBN 9781925022032.