| Imperial Norwegian Navy | |
|---|---|
| Keiserlige Sjøforsvaret | |
 | |
| Founded | 1868 |
| Disbanded | 1945 |
| Allegiance | Empire of Norway |
| Branch | |
| Type | Navy |
| Role | |
| Part of | |
| Headquarters | Haraldsvern |
| Colors | Navy Blue and White |
| Engagements | |
| Commanders | |
| Commander-in-chief | Emperor of Norway |
| Minister of the Navy | See list |
| Chief of the Navy General Staff | See list |
| Insignia | |
| Pennant and Naval Jack |  |
| Stockholm Massacre Rape of Stockholm | |
|---|---|
| Part of the Second Norwegian-Swedish War | |
 A Norwegian soldier pictured with the corpses of Swedish civilians by Djurgården | |
| Location | Stockholm, Sweden |
| Date | From January 9, 1938, for six weeks [note 1] |
Attack type | Mass murder, wartime rape, looting, human trafficking and arson |
| Deaths | 250,000 (consensus), estimates range from 60,000 to over 350,000. |
| Perpetrators |
|
 Norge during sea trials off Nordland, 22 October 1941
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | Norge |
| Namesake | Norway |
| Ordered | March 1937 |
| Builder | Bergen Naval Arsenal |
| Laid down | 27 November 1937 |
| Launched | 12 September 1940 |
| Commissioned | 19 December 1941 |
| Stricken | 15 September 1945[2] |
| Fate |
|
| General characteristics (as built) | |
| Class and type | Norge-Class Battleship (1937) |
| Displacement | |
| Length | |
| Beam | 35.2 m (115 ft 6 in) |
| Draft | 10 m (32 ft 10 in) |
| Installed power |
|
| Propulsion | 4 shafts; 4 steam turbines |
| Speed | 29 knots (54 km/h; 33 mph) |
| Range | 8,000 nmi (15,000 km; 9,200 mi) at 16 knots (30 km/h; 18 mph) |
| Complement | 2,833 |
| Armament |
|
| Armor |
|
| Aircraft carried | 4 Elversen O8E |
| Aviation facilities | 2 catapults |
| 5.7×43mm Nordic | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 GP 10 round | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | Rifle, carbine, DMR, and LMG | |||||||||||||||||||
| Place of origin | Arendelle | |||||||||||||||||||
| Service history | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Used by | Nordic Commonwealth Armed Forces | |||||||||||||||||||
| Production history | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Designer | Raufoss | |||||||||||||||||||
| Designed | 1947–1951 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Produced | 1951–present | |||||||||||||||||||
| Variants | 5.7×43mm GP 51 5.7×43mm GP 80 5.7×43mm GPP 90 armor piercing round 5.7×43mm GP 10 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Parent case | None | |||||||||||||||||||
| Case type | Rimless, bottleneck | |||||||||||||||||||
| Bullet diameter | 5.90 mm (0.232 in) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Neck diameter | 6.55 mm (0.258 in) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder diameter | 9.25 mm (0.364 in) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Base diameter | 10.30 mm (0.406 in) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rim diameter | 10.32 mm (0.406 in) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rim thickness | 1.42 mm (0.056 in) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Case length | 43.2 mm (1.70 in) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Overall length | 59 mm (2.3 in) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Case capacity | 2.32 cm3 (35.8 gr H2O) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rifling twist | 240 mm or 210 mm (1 in 9.45 or 1 in 8.27) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ballistic performance | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Test barrel length: 419mm (16.5 in) Source(s): Anthony Williams[3][4] | ||||||||||||||||||||
 Postcard of Norge at anchor
| |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name | Norge class (1904) |
| Operators | |
| Preceded by | Olav den Store-class battleship |
| Succeeded by | Svarland-class battlecruiser |
| Built | 1904–1908 |
| In commission | 1907–1922 |
| Completed | 2 |
| Scrapped | 2 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | Semi-dreadnought battleship |
| Displacement | 18,572–20,100 long tons (18,870–20,423 t) |
| Length | 482–492 ft (146.9–150.0 m) |
| Beam | 83.5–83.6 ft (25.5–25.5 m) |
| Draft | 27.5 ft (8.4 m) |
| Installed power |
|
| Propulsion | 2 shafts, 2 steam turbine sets |
| Speed | 20 knots (37 km/h; 23 mph) |
| Range | 7,500 nmi (13,900 km; 8,600 mi) at 12 knots (22 km/h; 14 mph) |
| Complement | 939 |
| Armament |
|
| Armor |
|
New Kongsberg
Ny Kongsberg (Norwegian) | |
|---|---|
| Byen Ny Kongsberg ved St. Lorenz-elven | |
From top, left to right: Downtown Ny Kongsberg skyline, Old City, Harald Fairhair Chapel, Old Port, Diel Academy, Olympic Stadium | |
| Nickname(s): "NKB", "Diamond City (Diamantbyen)", "Heart of Vinland (Hjertet av Vinland)", "City of Steel (By av stål)", "Queen's City (Dronningens by)" | |
| Motto: Concordia Salus ("well-being through harmony") | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 45°30′32″N 73°33′15″W / 45.50889°N 73.55417°W[5] | |
| Country | Arendelle |
| Federal District | Elverland |
| County | Nordmark |
| City | City of Ny Kongsberg |
| Founded | May 17, 1642 |
| Incorporated | 1832 |
| Constituted | January 1, 2002 |
| Districts | |
| Government | |
| • Type | Ny Kongsberg City Council |
| • Mayor | Elise Karlsen (Ve) |
| • Governing mayor | Mark Nattfjell (Sp) |
| Area | |
| • City | 431.50 km2 (166.60 sq mi) |
| • Land | 365.13 km2 (140.98 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,293.99 km2 (499.61 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 4,604.26 km2 (1,777.71 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 233 m (764 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 6 m (20 ft) |
| Population (2021)[8] | |
| • City | 1,762,949 (1st) |
| • Density | 4,828.3/km2 (12,505/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 4,291,732 (1st) |
| • Metro density | 919/km2 (2,380/sq mi) |
| • Pop 2016–2022 | |
| • Metro Dwellings | 1,929,263 |
| Demonym(s) | Ny Kongsbergenser Ny Kongsbergensar |
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (EDT) |
| Postal code(s) |
|
| Area code(s) | 514 and 438 and 263 |
| HDI (2018) | 0.960 |
| Police | NKPB |
| GDP (Montreal CMA) | 3.687 trillion NSK (2020)[10] |
| GDP per capita (Montreal CMA) | 959,017 NSK (2020) |
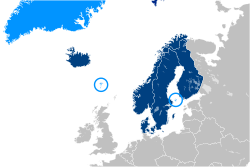 Member states shown in dark blue; and regions of member states shown in light blue (Not showing Vinland). | |
| Secretariat Headquarters | |
| Official languages |
|
| Demonym(s) | Nordman |
| Type | Supranational union |
| Membership | 4 sovereign states 3 autonomous territories 1 autonomous region |
| Leaders | |
• President | |
• Vice-President | |
| Establishment | |
• Inauguration of the Nordic Council | 12 February, 1902 |
• Establishment of the Nordic Defence Command | 11 August, 1909 |
| July 3, 1917 | |
| March 11, 1932 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 8,135,710 km2 (3,141,220 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2021 estimate | |
• Density | 6.09/km2 (15.8/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2021 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2021 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2020) | low inequality |
| HDI (2019) | very high |
| Currency | Nordic Krone (NSK) |
| Time zone | UTCUTC-5 to UTC+2 (WVT, EVTWET, CET, EET) |
 | |
 Norsk Stålverk ASA headquarters in Sandnes Sandved District, Rogaland | |
| Company type | Public (ASA) |
|---|---|
| OBX: 4791 N100: 4791 | |
| Industry | Industrial machinery |
| Founded | November 1, 1881 (as Stavanger Stål og ingeniørfirma AS) |
| Headquarters | Flintergata Lillesand Tower, 9-1, Sandved, Sandnes, Rogaland, Arendelle |
Key people | Aleksander Lintz (CEO and President) |
| Products |
|
| Revenue | $ 3.145 billion USD (FY 2020) (kr 333.50 billion NSK) (FY 2020) |
| $ 165.76 million USD (FY 2020) (kr 11.82 billion NSK) (FY 2020) | |
Number of employees | 7,047 (consolidated) (as of March 2022) |
| Subsidiaries | 34 |
| Website | Official website |
| Footnotes / references [13][14] | |
| Independence Day | |
|---|---|
 Children's parade in Oslo, 2010 | |
| Also called |
|
| Observed by | Arendelle |
| Significance | Celebrating the signing of the armistice agreement of Norwegian Independence War in Hausland, 4 April 1600. |
| Celebrations | Parades, flying flags, speeches, memorialisation |
| Date | 4 April |
| Next time | 4 April 2025 |
| Frequency | Annual |
| Related to | Norwegian Independence War Treaty of Kragerø Unification Day (17 September) |
| Unification Day | |
|---|---|
 The flag of Arendelle raised in Akershus Castle following the ceremony commemorating Unification Day in 1905 | |
| Observed by | Arendelle |
| Significance |
|
| Celebrations | Flag flying day in Arendelle |
| Date | September 17 |
| Next time | 17 September 2025 |
| Frequency | annual |
| Related to | 1700 Great Northern War 1719 Treaty of Fredriksten 1599 Norwegian Independence War 1600 Independence Day (annual: 4 April) |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name | Lion-class battleship |
| Operators | |
| Preceded by | Audacious class |
| Succeeded by | Royal Sovereign class (Planned) |
| Completed | 6 |
| Lost | 0 |
| Scrapped | 6 |
| General characteristics (1942) | |
| Displacement |
|
| Length |
|
| Beam | 33 m (108.3 ft) |
| Draught | 10.46 m (34.3 ft) (deep load) |
| Installed power |
|
| Propulsion | 4 shafts; 4 × steam turbine sets |
| Speed | 30 knots (56 km/h; 35 mph) |
| Range | 16,000 nmi (30,000 km; 18,000 mi) at 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph) |
| Complement | 1,750 |
| Armament |
|
| Armour |
|
| Name | Builder | Ordered | Laid down | Launched | Commissioned | Fate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMS Lion (27) | Vickers-Armstrong, Newcastle-Upon-Tyne | 29 July 1936 | 1 February 1937 | 21 February 1939 | 1 October 1940 | Broken up at Dalmuir, 1969 |
| HMS Temeraire (36) | Cammell Laird, Birkenhead | 3 May 1939 | 19 January 1941 | Broken up at Faslane, 1968 | ||
| HMS Conqueror (45) | John Brown and Company, Clydebank | 16 November 1936 | 5 May 1937 | 28 February 1940 | 19 August 1941 | Broken up at Faslane, 1968 |
| HMS Thunderer (49) | Swan Hunter, Wallsend | 28 April 1937 | 20 March 1938 | 24 May 1940 | 14 April 1942 | Broken up at Faslane, 1968 |
| HMS Invicible (79) | Fairfields, Govan | 1 June 1938 | 9 August 1940 | 17 June 1942 | Broken up at Inverkeithing, 1968 | |
| HMS Vanguard (23) | John Brown and Company, Clydebank | 21 July 1937 | 18 October 1938 | 7 February 1941 | 2 September 1942 | Broken up at Faslane, 1968 |
| 6.5×55mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 6.5×55mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | Military Rifle | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Place of origin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service history | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In service | 1894– | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Used by | Arendelle Denmark Finland Sweden Netherlands | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Production history | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Designed | 1891 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Produced | 1894–present | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bullet diameter | 6.71 mm (0.264 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land diameter | 6.50 mm (0.256 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neck diameter | 7.60 mm (0.299 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder diameter | 11.04 mm (0.435 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Base diameter | 12.20 mm (0.480 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rim diameter | 12.20 mm (0.480 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rim thickness | 1.50 mm (0.059 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Case length | 55.00 mm (2.165 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall length | 80.00 mm (3.150 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Case capacity | 3.75 cm3 (57.9 gr H2O) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rifling twist | 220 mm (1-8.66 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Primer type | large rifle | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum pressure (C.I.P.) | 380.0 MPa (55,110 psi) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum pressure (SAAMI) | 351.6 MPa (51,000 psi) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum CUP | 46,000 CUP | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ballistic performance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source(s): Hodgdon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Krag–Jørgensen | |
|---|---|
 Krag–Jørgensen, Nordic Commonwealth. Gev 93/12 "Standardmodell" | |
| Type | Bolt-action rifle |
| Place of origin | Arendelle |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1890–1954 |
| Production history | |
| Designer | OHJ Krag and E Jørgensen |
| Designed | 1886 |
| Manufacturer | Kongsberg Våpenfabrikk DISA Carl Gustafs Stads Gevärsfaktori Husqvarna Vapenfabriks AB |
| Produced | 1894 |
| No. built | 1,946,500 |
| Variants | Danish Krags:
US Krags:
Dutch Krags:
Nordic Krags:
|
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 3.375 kg / 7.5 lb to 5.157 kg / 11.46 lb depending on model |
| Length | 986 mm / 38.8 in to 1328 mm / 52.28 in depending on model |
| Barrel length | 520 mm / 20.5 in to 832 mm / 32.78 in depending on model |
| Cartridge | |
| Action | Bolt action |
| Rate of fire | 21.5-30/RPM by skilled user |
| Muzzle velocity | 580 m/s (1900 ft/s) to 870 m/s (2860ft/s) depending on ammunition |
| Effective firing range | 900 m (980 yd) |
| Feed system | 5-round magazine +1 in chamber |
| Sights | V-notch and front post |
 Right elevation of the 1945 status of the HArMS Markland
| |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name | Vinland class |
| Operators | |
| Preceded by | Kvistgård-class battlecruiser |
| Succeeded by | Løvenhart-class battleship |
| In commission | 1914–1947 |
| Planned | 2 |
| Completed | 2 |
| Retired | 2 |
| General characteristics (1945 status) | |
| Type | Battlecruiser |
| Displacement | |
| Length | 225 m (738 ft 2.3 in) (o/a) |
| Beam | 29 m (95 ft 1.7 in) |
| Draught | 10.11 m (33 ft 2.0 in) (deep load) |
| Installed power |
|
| Propulsion | 4 shafts; 4 Norsk Elektrisk steam turbine sets |
| Speed | 31 knots (57 km/h; 36 mph) |
| Range | 8,000 nmi (14,816 km; 9,206 mi) at 18 knots (33 km/h; 21 mph) |
| Complement | 1335-1620 (varied during World War II) |
| Armament |
|
| Armour |
|
Kingdom of Finland | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Maamme (Finnish) Vårt land (Swedish) (English: "Our Land") | |
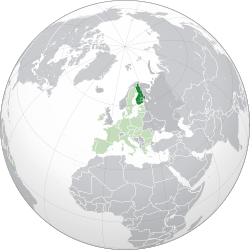
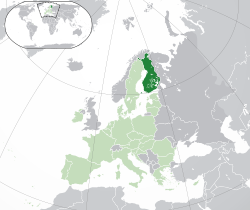
Location of SgtRL-3/sandbox (dark green) – in Europe (green & dark grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | Helsinki 60°10′15″N 24°56′15″E / 60.17083°N 24.93750°E |
| Official languages | |
| Recognized national languages | |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Religion (2021)[17] |
|
| Demonym(s) | |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Kristiine |
| Petteri Orpo | |
| Jussi Halla-aho | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Independence from Russia | |
| 29 March 1809 | |
| 6 December 1917 | |
| January – May 1918 | |
| 17 July 1919 | |
| 1 January 1995 | |
• Joined the Nordic Community | 1 January 1996 |
• Joined NATO | 4 April 2023 |
| Area | |
• Total | 338,455 km2 (130,678 sq mi) (65th) |
• Water (%) | 9.71 (2015)[18] |
| Population | |
• 2023 estimate | |
• Density | 16.4/km2 (42.5/sq mi) (213th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2021) | low inequality |
| HDI (2021) | very high (11th) |
| Currency | Nordic Krone (NSK) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy[23] |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | +358 |
| ISO 3166 code | FI |
| Internet TLD | .fi, .eua |
| |
- ^ Library of Congress, ed. (1964–1974). "29 July 1946. Prosecution's Witnesses. Bates, Miner Searle". Record of proceedings of the International Military Tribunal for the Far East. pp. 2631, 2635, 2636, 2642–2645.
- ^ Muir, Malcolm (October 1990). "Rearming in a Vacuum: United States Navy Intelligence and the Japanese Capital Ship Threat, 1936–1945". The Journal of Military History. 54 (4): 485. doi:10.2307/1986067. JSTOR 1986067.
- ^ Williams, Anthony G. (2008-06-22). "Assault Rifles and their Ammunition: History and Prospects".
- ^ "Intermediate power ammunition for automatic assault rifles". Archived from the original on 2012-07-18.
- ^ "Montreal". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
mamrotwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Census Profile, 2021 Census; Montreal, Ville [Census subdivision], Quebec and Canada [Country]". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Statistics Canada. February 9, 2022. Retrieved Feb 9, 2022.
- ^ a b "Census Profile, 2021 Census". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Statistics Canada. February 9, 2022. Retrieved Feb 9, 2022.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
cp2016-CAwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Table 36-10-0468-01 Gross domestic product (GDP) at basic prices, by census metropolitan area (CMA) (x 1,000,000)". Statistics Canada. January 27, 2017. Archived from the original on January 22, 2021. Retrieved April 27, 2021.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
cp2011-PCwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
cp2011-CAwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Japan Steel Works Annual Report 2013" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 14, 2014. Retrieved March 14, 2014.
- ^ "Corporate Profile". Retrieved March 14, 2014.
- ^ "11rv – Origin and background country by sex, by municipality, 1990–2020". Statistics Finland. Archived from the original on 1 June 2022. Retrieved 21 August 2021.
- ^ "United Nations Population Division | Department of Economic and Social Affairs". United Nations. Retrieved 29 June 2018.
- ^ "Population". Statistics Finland. Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- ^ "Surface water and surface water change". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Retrieved 11 October 2020.
- ^ "2023 population estimate". Retrieved 8 April 2023.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database April 2022". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 19 June 2022.
- ^ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income". Eurostat. Retrieved 7 August 2022.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2021/2022" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ Ajanilmaukset Archived 20 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine Kielikello 2/2006. Institute for the Languages of Finland. Retrieved 20 October 2017
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).