Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
The Classical Music Portal


Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" can also be applied to non-Western art musics. Classical music is often characterized by formality and complexity in its musical form and harmonic organization, particularly with the use of polyphony. Since at least the ninth century it has been primarily a written tradition, spawning a sophisticated notational system, as well as accompanying literature in analytical, critical, historiographical, musicological and philosophical practices. A foundational component of Western culture, classical music is frequently seen from the perspective of individual or groups of composers, whose compositions, personalities and beliefs have fundamentally shaped its history. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1The Royal Academy of Music (RAM) in London, England, is one of the oldest music schools in the UK, founded in 1822 by John Fane and Nicolas-Charles Bochsa. It received its royal charter in 1830 from King George IV with the support of the first Duke of Wellington.
The academy provides undergraduate and postgraduate training across instrumental performance, composition, jazz, musical theatre and opera, and recruits musicians from around the world, with a student community representing more than 50 nationalities. It is committed to lifelong learning, from Junior Academy, which trains musicians up to the age of 18, through Open Academy community music projects, to performances and educational events for all ages. (Full article...) -
Image 2

Rita Sangalli as Sylvia in the 1876 production of the ballet
Sylvia, originally Sylvia, ou La nymphe de Diane, is a full-length classical ballet in two or three acts, first choreographed by Louis Mérante to music by Léo Delibes.
The ballet's premiere took place on 14 June 1876 at the Palais Garnier, but was largely unnoticed by the critics. The first seven productions were commercially unsuccessful, but the 1952 revival, choreographed by Frederick Ashton, popularized the work. Productions in 1997, 2004, 2005, and 2009 productions were all based on Ashton's choreography. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Beginning of BWV 565 in Johannes Ringk's manuscript, which is, as far as known, the only extant 18th-century copy of the work
The Toccata and Fugue in D minor, BWV 565, is a composition for organ by, according to the oldest sources, German composer Johann Sebastian Bach and is one of the most widely recognisable works in the organ repertoire. Although the date of its origin is unknown, scholars have suggested between 1704 and the 1750s. The piece opens with a toccata section followed by a fugue that ends in a coda, and is largely typical of the north German organ school of the Baroque era.
Little was known about its early existence until the piece was discovered in an undated manuscript produced by Johannes Ringk. It was first published in 1833 during the early Bach Revival period through the efforts of composer Felix Mendelssohn, who also performed the piece in 1840. It was not until the 20th century that its popularity rose above that of other organ compositions by Bach, as exemplified by its inclusion in Walt Disney's 1940 animated film Fantasia that featured Leopold Stokowski's orchestral transcription from 1927. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Portrait by Anton Depauly, of Schubert at the end of his life
Franz Schubert's last three piano sonatas, D 958, 959 and 960, are his last major compositions for solo piano. They were written during the last months of his life, between the spring and autumn of 1828, but were not published until about ten years after his death, in 1838–39. Like the rest of Schubert's piano sonatas, they were mostly neglected in the 19th century. By the late 20th century, however, public and critical opinion had changed, and these sonatas are now considered among the most important of the composer's mature masterpieces. They are part of the core piano repertoire, appearing regularly on concert programs and recordings.
One of the reasons for the long period of neglect of Schubert's piano sonatas seems to be their dismissal as structurally and dramatically inferior to the sonatas of Beethoven. In fact, the last sonatas contain distinct allusions and similarities to works by Beethoven, a composer Schubert venerated. Nevertheless, musicological analysis has shown that they maintain a mature, individual style. The last sonatas are now praised for that mature style, manifested in unique features such as a cyclical formal and tonal design, chamber music textures, and a rare depth of emotional expression. (Full article...) -
Image 5A countertenor (also contra tenor) is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range is equivalent to that of the female contralto or mezzo-soprano voice types, generally extending from around G3 to D5 or E5, although a sopranist (a specific kind of countertenor) may match the soprano's range of around C4 to C6. Countertenors often have tenor or baritone chest voices, but sing in falsetto or head voice much more often than they do in their chest voice.
The nature of the countertenor voice has radically changed throughout musical history, from a modal voice, to a modal and falsetto voice, to the primarily falsetto voice that is denoted by the term today. This is partly because of changes in human physiology (increase in body height) and partly because of fluctuations in pitch. (Full article...) -
Image 6Ida Rubinstein, who commissioned Boléro, in 1922
Boléro is a 1928 work for large orchestra by French composer Maurice Ravel. It is one of Ravel's most famous compositions. It was also one of his last completed works before illness diminished his ability to write music. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Macbeth at the Savonlinna Opera Festival in St. Olaf's Castle, Savonlinna, Finland, in 2007
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librettist and incorporates a number of the performing arts, such as acting, scenery, costume, and sometimes dance or ballet. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble, which since the early 19th century has been led by a conductor. Although musical theatre is closely related to opera, the two are considered to be distinct from one another.
Opera is a key part of Western classical music, and Italian tradition in particular. Originally understood as an entirely sung piece, in contrast to a play with songs, opera has come to include, including some that include spoken dialogue such as Singspiel and Opéra comique. In traditional number opera, singers employ two styles of singing: recitative, a speech-inflected style, and self-contained arias. The 19th century saw the rise of the continuous music drama. (Full article...) -
Image 8
Sergei Vasilyevich Rachmaninoff (1 April [O.S. 20 March] 1873 – 28 March 1943) was a Russian composer, virtuoso pianist, and conductor. Rachmaninoff is widely considered one of the finest pianists of his day and, as a composer, one of the last great representatives of Romanticism in Russian classical music. Early influences of Tchaikovsky, Rimsky-Korsakov, and other Russian composers gave way to a thoroughly personal idiom notable for its song-like melodicism, expressiveness, dense contrapuntal textures, and rich orchestral colours. The piano is featured prominently in Rachmaninoff's compositional output and he used his skills as a performer to fully explore the expressive and technical possibilities of the instrument.
Born into a musical family, Rachmaninoff began learning the piano at the age of four. He studied piano and composition at the Moscow Conservatory, from which he graduated in 1892, having already written several compositions. In 1897, following the disastrous premiere of his Symphony No. 1, Rachmaninoff entered a four-year depression and composed little, until supportive therapy allowed him to complete his well-received Piano Concerto No. 2 in 1901. Rachmaninoff went on to become conductor of the Bolshoi Theatre from 1904–1906, and relocated to Dresden, Germany, in 1906. He later embarked upon his first tour of the United States as a pianist in 1909. (Full article...) -
Image 9

Portrait of Haydn by Thomas Hardy, c. 1791
Franz Joseph Haydn (/ˈhaɪdən/ HY-dən; German: [ˈfʁants ˈjoːzɛf ˈhaɪdn̩] ⓘ; 31 March 1732 – 31 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions to musical form have led him to be called "Father of the Symphony" and "Father of the String quartet".
Haydn spent much of his career as a court musician for the wealthy Esterházy family at their Eszterháza Castle. Until the later part of his life, this isolated him from other composers and trends in music so that he was, as he put it, "forced to become original". Yet his music circulated widely, and for much of his career he was the most celebrated composer in Europe. (Full article...) -
Image 10
Johannes Brahms (/brɑːmz/; German: [joˈhanəs ˈbʁaːms]; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, virtuoso pianist, and conductor of the mid-Romantic period. His music is rooted in the structures and compositional techniques of his Classical (and earlier) forebears, including Ludwig van Beethoven and Johann Sebastian Bach. His compositions include four symphonies, four concertos, a Requiem, and many songs, amongst other music for symphony orchestra, piano, organ, voices, and chamber ensembles. They remain a staple of the concert repertoire.
Born to a musical family in Hamburg, he composed in his youth, concertizing locally. He toured Central Europe as a pianist in his early adulthood, working with Ede Reményi and Joseph Joachim, meeting Franz Liszt in Weimar, and premiering many of his own works. He was self-conscious and could be severely self-critical, but his music was largely successful. It gradually formed the basis for a growing circle of supporters, friends, and musicians. With Joachim's assistance, Brahms sought Robert Schumann's approval, receiving both his and Clara Schumann's vigorous support and guidance. Robert and later Hans von Bülow even cast him as Beethoven's musical heir. After Brahms's rued emergence counter to him in the War of the Romantics, Richard Wagner mocked this idea. (Full article...) -
Image 11Mendelssohn in 1846 by Eduard Magnus
Felix Mendelssohn's Violin Concerto in E minor, Op. 64, MWV O 14, is his last concerto. Well received at its premiere, it has remained among the most prominent and highly-regarded violin concertos. It holds a central place in the violin repertoire and has developed a reputation as an essential concerto for all aspiring concert violinists to master, and usually one of the first Romantic era concertos they learn. A typical performance lasts just under half an hour.
Mendelssohn originally proposed the idea of the violin concerto to Ferdinand David, a close friend and then concertmaster of the Leipzig Gewandhaus Orchestra. Although conceived in 1838, the work took another six years to complete and was not premiered until 1845. During this time, Mendelssohn maintained a regular correspondence with David, who gave him many suggestions. The work itself was one of the foremost violin concertos of the Romantic era and was influential on many other composers. (Full article...) -
Image 12Johann Christoph von Ponickau, for whose memorial service the cantata was composed
Ich lasse dich nicht, du segnest mich denn (I will not let you go, unless you bless me), BWV 157, is a church cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. He composed it in Leipzig in 1726/27 to a libretto by Picander. The first known performance was on 6 February 1727 during a memorial service for Johann Christoph von Ponickau in Pomßen near Leipzig. The work was later assigned to the feast of the Purification celebrated on 2 February.
Picander included a quotation from Genesis 32:26–32 in the first movement, and the last stanza of Christian Keymann's "Meinen Jesum laß ich nicht" in the closing chorale. The contemplation begins with the Old Testament quotation being applied to Jesus, and leads to the last aria expressing an eager wish for death to arrive soon. The closing chorale picks up the first line. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
Image 1Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, posthumous painting by Barbara Krafft in 1819 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 2Fortepiano by Paul McNulty after Walter & Sohn, c. 1805 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 4The opening bars of the Commendatore's aria in Mozart's opera Don Giovanni. The orchestra starts with a dissonant diminished seventh chord (G# dim7 with a B in the bass) moving to a dominant seventh chord (A7 with a C# in the bass) before resolving to the tonic chord (D minor) at the singer's entrance. (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 5Portion of Du Fay's setting of Ave maris stella, in fauxbourdon. The top line is a paraphrase of the chant; the middle line, designated "fauxbourdon", (not written) follows the top line but exactly a perfect fourth below. The bottom line is often, but not always, a sixth below the top line; it is embellished, and reaches cadences on the octave.Play (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 6Marc-Antoine Charpentier (from Baroque music)
-
Image 7Gustav Mahler, photographed in 1907 by Moritz Nähr at the end of his period as director of the Vienna Hofoper (from Romantic music)
-
Image 8Double-manual harpsichord by Vital Julian Frey, after Jean-Claude Goujon (1749) (from Baroque music)
-
Image 12A group of Renaissance musicians in The Concert (1623) by Gerard van Honthorst (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 14A young Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, a representative composer of the Classical period, seated at a keyboard. (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 15Richard Wagner in Paris, 1861
-
Image 16Josef Danhauser's 1840 painting of Franz Liszt at the piano surrounded by (from left to right) Alexandre Dumas, Hector Berlioz, George Sand, Niccolò Paganini, Gioachino Rossini and Marie d'Agoult, with a bust of Ludwig van Beethoven on the piano (from Romantic music)
-
Image 22A large instrumental ensemble's performance in the lavish Teatro Argentina, as depicted by Panini (1747) (from Baroque music)
-
Image 23Hummel in 1814 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 24Musicians from 'Procession in honour of Our Lady of Sablon in Brussels.' Early 17th-century Flemish alta cappella. From left to right: bass dulcian, alto shawm, treble cornett, soprano shawm, alto shawm, tenor sackbut. (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 25Wanderer above the Sea of Fog, by Caspar David Friedrich, is an example of Romantic painting. (from Romantic music)
-
Image 27Individual sheet music for a seventeenth-century harp. (from Baroque music)
-
Image 301875 oil painting of Franz Schubert by Wilhelm August Rieder, after his own 1825 watercolor portrait (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 31Balakirev (top), Cui (upper left), Mussorgsky (upper right), Rimsky-Korsakov (lower left), and Borodin (lower right). (from Romantic music)
-
Image 32Gluck, detail of a portrait by Joseph Duplessis, dated 1775 (Kunsthistorisches Museum, Vienna) (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 34Bernhard Crusell, a Swedish-Finnish composer and clarinetist, in 1826 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 35A modern string quartet. In the 2000s, string quartets from the Classical era are the core of the chamber music literature. From left to right: violin 1, violin 2, cello, viola (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 36Painting by Evaristo Baschenis of Baroque instruments, including a cittern, viola da gamba, violin, and two lutes (from Baroque music)
-
Image 37The Mozart family c. 1780. The portrait on the wall is of Mozart's mother. (from Classical period (music))
Quotes - show another
| “ | Emphasis on the common emotive or affective origins of music and words in the first cries of humankind undermines words. | ” |
| — Jean Philippe Rameau | ||
Related portals
WikiProjects
 Selected composers - load new batch
Selected composers - load new batch 
-
Image 1

Charles-Valentin Alkan, c. 1835. Portrait by Édouard Dubufe
Charles-Valentin Alkan (French: [ʃaʁl valɑ̃tɛ̃ alkɑ̃]; 30 November 1813 – 29 March 1888) was a French composer and virtuoso pianist. At the height of his fame in the 1830s and 1840s he was, alongside his friends and colleagues Frédéric Chopin and Franz Liszt, among the leading pianists in Paris, a city in which he spent virtually his entire life.
Alkan earned many awards at the Conservatoire de Paris, which he entered before he was six. His career in the salons and concert halls of Paris was marked by his occasional long withdrawals from public performance, for personal reasons. Although he had a wide circle of friends and acquaintances in the Parisian artistic world, including Eugène Delacroix and George Sand, from 1848 he began to adopt a reclusive life style, while continuing with his compositions – virtually all of which are for the keyboard. During this period he published, among other works, his collections of large-scale studies in all the major keys (Op. 35) and all the minor keys (Op. 39). The latter includes his Symphony for Solo Piano (Op. 39, nos. 4–7) and Concerto for Solo Piano (Op. 39, nos. 8–10), which are often considered among his masterpieces and are of great musical and technical complexity. Alkan emerged from self-imposed retirement in the 1870s to give a series of recitals that were attended by a new generation of French musicians. (Full article...) -
Image 2

Stanford in 1921
Sir Charles Villiers Stanford (30 September 1852 – 29 March 1924) was an Anglo-Irish composer, music teacher, and conductor of the late Romantic era. Born to a well-off and highly musical family in Dublin, Stanford was educated at the University of Cambridge before studying music in Leipzig and Berlin. He was instrumental in raising the status of the Cambridge University Musical Society, attracting international stars to perform with it.
While still an undergraduate, Stanford was appointed organist of Trinity College, Cambridge. In 1882, aged 29, he was one of the founding professors of the Royal College of Music, where he taught composition for the rest of his life. From 1887 he was also Professor of Music at Cambridge. As a teacher, Stanford was sceptical about modernism, and based his instruction chiefly on classical principles as exemplified in the music of Brahms. Among his pupils were rising composers whose fame went on to surpass his own, such as Gustav Holst and Ralph Vaughan Williams. As a conductor, Stanford held posts with the Bach Choir and the Leeds Triennial Music Festival. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Cabinet card of Massenet by Eugène Pirou, 1895
Jules Émile Frédéric Massenet (French pronunciation: [ʒyl emil fʁedeʁik masnɛ]; 12 May 1842 – 13 August 1912) was a French composer of the Romantic era best known for his operas, of which he wrote more than thirty. The two most frequently staged are Manon (1884) and Werther (1892). He also composed oratorios, ballets, orchestral works, incidental music, piano pieces, songs and other music.
While still a schoolboy, Massenet was admitted to France's principal music college, the Paris Conservatoire. There he studied under Ambroise Thomas, whom he greatly admired. After winning the country's top musical prize, the Prix de Rome, in 1863, he composed prolifically in many genres, but quickly became best known for his operas. Between 1867 and his death forty-five years later he wrote more than forty stage works in a wide variety of styles, from opéra-comique to grand-scale depictions of classical myths, romantic comedies, lyric dramas, as well as oratorios, cantatas and ballets. Massenet had a good sense of the theatre and of what would succeed with the Parisian public. Despite some miscalculations, he produced a series of successes that made him the leading composer of opera in France in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Mykola Leontovych
Mykola Dmytrovych Leontovych (Ukrainian: Микола Дмитрович Леонтович, pronounced [mɪˈkɔlɐ dmɪˈtrɔʋet͡ʃ ɫeɔnˈtɔʋet͡ʃ] ⓘ; 13 December [O.S. 1 December] 1877 – 23 January 1921) was a Ukrainian composer, conductor, ethnomusicologist, and teacher. His music was inspired by the Ukrainian composer Mykola Lysenko and the Ukrainian National Music School. Leontovych specialised in a cappella choral music, ranging from original compositions to church music to elaborate arrangements of folk music.
Leontovych was born and raised in Monastyrok in the Podolia province of the Russian Empire (now in Vinnytsia Oblast, Western Ukraine). He was educated as a priest in the Kamianets-Podilskyi Theological Seminary. With the independence of the Ukrainian State in the 1917 revolution, he moved to Kyiv, where he worked at the Kyiv Conservatory and the Mykola Lysenko Institute of Music and Drama. He composed "Shchedryk" in 1904 (premiered in 1916), now known to the English-speaking world as "Carol of the Bells". He was murdered by a Soviet agent in 1921 and is known as a martyr in the Eastern Orthodox Ukrainian Church, where he is also remembered for his liturgy, the first composed in the vernacular, specifically in the modern Ukrainian language. (Full article...) -
Image 5

The organ at Exeter Cathedral, which Gibbons may have played
Edward Gibbons (bapt. 21 March 1568 – in or before July 1650) was an English choirmaster and composer of the late Renaissance and early Baroque periods. Born in Cambridge, Gibbons's youth is completely unknown, but he later received degrees from the Universities of Cambridge and Oxford. From 1591/92 to 1598 he worked at King's College, Cambridge, as a lay clerk and choirmaster. During his tenure he married Jane, with whom he had six children. Gibbons's whereabouts the next few years remain uncertain; he may have lived in Acton, Bristol or Exeter, but by 1607 he was the choirmaster of the Exeter Cathedral, where the choristers included Matthew Locke. By 1609 Gibbons received a special dispensation to become a priest vicar, becoming the head of the college of priest-vicars and succentor. Jane died in 1628, and Edward married Mary Bluet; the family was evicted from their home during the English Civil War, but moved to their estate in Dunsford.
A few compositions of Gibbons survive: an organ prelude, two verse anthems, two works for viol consorts, and some sacred music. Of these, commentators have mainly praised the verse anthems, How hath ye City sate solitary and What Strikes the Clocke? Musicologist John Harley called the former particularly moving, and it was likely written for the 1603 London plague outburst to which Gibbons's brother Ellis may have succumbed to. Edward is the elder brother of the better-known Orlando; after the early deaths of Orlando and his wife, Edward cared for their son, Christopher, who also became a noted composer. (Full article...) -
Image 6Jane Marian Joseph (31 May 1894 – 9 March 1929) was an English composer, arranger and music teacher. She was a pupil and later associate of the composer Gustav Holst, and was instrumental in the organisation and management of various of the music festivals which Holst sponsored. Many of her works were composed for performance at these festivals and similar occasions. Her early death at age 35, which prevented the full realisation of her talents, was considered by her contemporaries as a considerable loss to English music.
Holst first observed Joseph's potential when he was teaching her composition at St Paul's Girls' School. She began to act as his amanuensis in 1914, when he was composing The Planets, her special responsibility being the preparation of the score for the "Neptune" movement. She continued to assist Holst with transcriptions, arrangements and translations, and was his librettist for the choral ballet The Golden Goose. (Full article...) -
Image 7Martin Peerson (or Pearson, Pierson, Peereson) (between 1571 and 1573 – December 1650 or January 1651 and buried 16 January 1651) was an English composer, organist and virginalist. Despite Roman Catholic leanings at a time when it was illegal not to subscribe to Church of England beliefs and practices, he was highly esteemed for his musical abilities and held posts at St Paul's Cathedral and, it is believed, Westminster Abbey. His output included both sacred and secular music in forms such as consort music, keyboard pieces, madrigals and motets. (Full article...)
-
Image 8

Bizet photographed by Étienne Carjat (1875)
Georges Bizet (né Alexandre César Léopold Bizet; 25 October 1838 – 3 June 1875) was a French composer of the Romantic era. Best known for his operas in a career cut short by his early death, Bizet achieved few successes before his final work, Carmen, which has become one of the most popular and frequently performed works in the entire opera repertoire.
During a brilliant student career at the Conservatoire de Paris, Bizet won many prizes, including the prestigious Prix de Rome in 1857. He was recognised as an outstanding pianist, though he chose not to capitalise on this skill and rarely performed in public. Returning to Paris after almost three years in Italy, he found that the main Parisian opera theatres preferred the established classical repertoire to the works of newcomers. His keyboard and orchestral compositions were likewise largely ignored; as a result, his career stalled, and he earned his living mainly by arranging and transcribing the music of others. Restless for success, he began many theatrical projects during the 1860s, most of which were abandoned. Neither of his two operas that reached the stage in this time—Les pêcheurs de perles and La jolie fille de Perth—were immediately successful. (Full article...) -
Image 9
Aram Ilyich Khachaturian (/ˈærəm ˌkɑːtʃəˈtʊəriən/; Russian: Арам Ильич Хачатурян, IPA: [ɐˈram ɨˈlʲjitɕ xətɕɪtʊˈrʲan] ⓘ; Armenian: Արամ Խաչատրյան, Aram Xačatryan; 6 June [O.S. 24 May] 1903 – 1 May 1978) was a Soviet Armenian composer and conductor. He is considered one of the leading Soviet composers.
Born and raised in Tbilisi (now the capital of Georgia), Khachaturian moved to Moscow in 1921 following the Sovietization of the Caucasus. Without prior music training, he enrolled in the Gnessin Musical Institute, subsequently studying at the Moscow Conservatory in the class of Nikolai Myaskovsky, among others. His first major work, the Piano Concerto (1936), popularized his name within and outside the Soviet Union. It was followed by the Violin Concerto (1940) and the Cello Concerto (1946). His other significant compositions include the Masquerade Suite (1941), the Anthem of the Armenian SSR (1944), three symphonies (1935, 1943, 1947), and around 25 film scores. Khachaturian is best known for his ballet music—Gayane (1942) and Spartacus (1954). His most popular piece, the "Sabre Dance" from Gayane, has been used extensively in popular culture and has been performed by a number of musicians worldwide. His style is "characterized by colorful harmonies, captivating rhythms, virtuosity, improvisations, and sensuous melodies". (Full article...) -
Image 10
Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy (3 February 1809 – 4 November 1847), widely known as Felix Mendelssohn, was a German composer, pianist, organist and conductor of the early Romantic period. Mendelssohn's compositions include symphonies, concertos, piano music, organ music and chamber music. His best-known works include the overture and incidental music for A Midsummer Night's Dream (which includes his "Wedding March"), the Italian Symphony, the Scottish Symphony, the oratorio St. Paul, the oratorio Elijah, the overture The Hebrides, the mature Violin Concerto, the String Octet, and the melody used in the Christmas carol "Hark! The Herald Angels Sing". Mendelssohn's Songs Without Words are his most famous solo piano compositions.
Mendelssohn's grandfather was the renowned Jewish philosopher Moses Mendelssohn, but Felix was initially raised without religion until he was baptised aged seven into the Reformed Christian church. He was recognised early as a musical prodigy, but his parents were cautious and did not seek to capitalise on his talent. His sister Fanny Mendelssohn received a similar musical education and was a talented composer and pianist in her own right; some of her early songs were published under her brother's name and her Easter Sonata was for a time mistakenly attributed to him after being lost and rediscovered in the 1970s. (Full article...) -
Image 11
Carl August Nielsen (Danish: [ˈkʰɑˀl ˈne̝lsn̩]; 9 June 1865 – 3 October 1931) was a Danish composer, conductor and violinist, widely recognized as his country's most prominent composer.
Brought up by poor yet musically talented parents on the island of Funen, he demonstrated his musical abilities at an early age. He initially played in a military band before attending the Royal Danish Academy of Music in Copenhagen from 1884 until December 1886. He premiered his Op. 1, Suite for Strings, in 1888, at the age of 23. The following year, Nielsen began a 16-year stint as a second violinist in the Royal Danish Orchestra under the conductor Johan Svendsen, during which he played in Giuseppe Verdi's Falstaff and Otello at their Danish premieres. In 1916, he took a post teaching at the Royal Danish Academy and continued to work there until his death. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Clarke with a viola in 1919
Rebecca Helferich Clarke (27 August 1886 – 13 October 1979) was a British classical composer and violist. Internationally renowned as a viola virtuoso, she also became one of the first female professional orchestral players in London.
Rebecca Clarke had German and American parents, and spent substantial periods of her life in the United States, where she permanently settled after World War II. She was born in Harrow and studied at the Royal Academy of Music and Royal College of Music in London. Stranded in the United States at the outbreak of World War II, she married composer and pianist James Friskin in 1944. Clarke died at her home in New York at the age of 93. (Full article...) -
Image 13
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev (27 April [O.S. 15 April] 1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, pianist, and conductor who later worked in the Soviet Union. As the creator of acknowledged masterpieces across numerous music genres, he is regarded as one of the major composers of the 20th century. His works include such widely heard pieces as the March from The Love for Three Oranges, the suite Lieutenant Kijé, the ballet Romeo and Juliet—from which "Dance of the Knights" is taken—and Peter and the Wolf. Of the established forms and genres in which he worked, he created—excluding juvenilia—seven completed operas, seven symphonies, eight ballets, five piano concertos, two violin concertos, a cello concerto, a symphony-concerto for cello and orchestra, and nine completed piano sonatas.
A graduate of the Saint Petersburg Conservatory, Prokofiev initially made his name as an iconoclastic composer-pianist, achieving notoriety with a series of ferociously dissonant and virtuosic works for his instrument, including his first two piano concertos. In 1915, Prokofiev made a decisive break from the standard composer-pianist category with his orchestral Scythian Suite, compiled from music originally composed for a ballet commissioned by Sergei Diaghilev of the Ballets Russes. Diaghilev commissioned three further ballets from Prokofiev—Chout, Le pas d'acier and The Prodigal Son—which, at the time of their original production, all caused a sensation among both critics and colleagues. But Prokofiev's greatest interest was opera, and he composed several works in that genre, including The Gambler and The Fiery Angel. Prokofiev's one operatic success during his lifetime was The Love for Three Oranges, composed for the Chicago Opera and performed over the following decade in Europe and Russia. (Full article...) -
Image 14

Imogen Clare Holst CBE (née von Holst; 12 April 1907 – 9 March 1984) was a British composer, arranger, conductor, teacher, musicologist, and festival administrator. The only child of the composer Gustav Holst, she is particularly known for her educational work at Dartington Hall in the 1940s, and for her 20 years as joint artistic director of the Aldeburgh Festival. In addition to composing music, she wrote composer biographies, much educational material, and several books on the life and works of her father.
From a young age, Holst showed precocious talent in composing and performance. After attending Eothen School and St Paul's Girls' School, she entered the Royal College of Music, where she developed her skills as a conductor and won several prizes for composing. Unable to follow her initial ambitions to be a pianist or a dancer for health reasons, Holst spent most of the 1930s teaching, and as a full-time organiser for the English Folk Dance and Song Society. These duties reduced her compositional activities, although she made many arrangements of folksongs. After serving as an organiser for the Council for the Encouragement of Music and the Arts at the start of the Second World War, in 1942 she began working at Dartington. In her nine years there she established Dartington as a major centre of music education and activity. (Full article...) -
Image 15
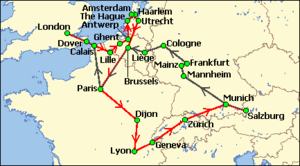
Map showing the Grand Tour, 1763–1766. Black line shows outward journey to London, 1763–1764. Red line shows homeward journey to Salzburg, 1765–1766. Occluded line shows travel in each direction.
The Mozart family grand tour was a journey through western Europe, undertaken by Leopold Mozart, his wife Anna Maria, and their children Maria Anna (Nannerl) and Wolfgang Theophilus (Wolferl) from 1763 to 1766. At the start of the tour the children were aged eleven and seven respectively. Their extraordinary skills had been demonstrated during a visit to Vienna in 1762, when they had played before the Empress Maria Theresa at the Imperial Court. Sensing the social and pecuniary opportunities that might accrue from a prolonged trip embracing the capitals and main cultural centres of Europe, Leopold obtained an extended leave of absence from his post as deputy Kapellmeister to the Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg. Throughout the subsequent tour, the children's Wunderkind status was confirmed as their precocious performances consistently amazed and gratified their audiences.
The first stage of the tour's itinerary took the family, via Munich and Frankfurt, to Brussels and then on to Paris where they stayed for five months. They then departed for London, where during a stay of more than a year Wolfgang made the acquaintance of some of the leading musicians of the day, heard much music, and composed his first symphonies. The family then moved on to the Netherlands, where the schedule of performances was interrupted by the illnesses of both children, although Wolfgang continued to compose prolifically. The homeward phase incorporated a second stop in Paris and a trip through Switzerland, before the family's return to Salzburg in November 1766. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) - load new batch

- ... that the Stadthalle Hannover, the largest classical music concert hall in Germany by capacity, was modelled after the Pantheon in Rome and completed by 1914?
- ... that the choral music of Artemy Vedel, who is regarded as one of the Golden Three composers of 18th-century Ukrainian classical music, was censored but performed from handwritten copies?
- ... that, according to its owner, KLEF in Anchorage, Alaska, was one of just three remaining commercially operated classical-music radio stations in the United States, as of 2013?
- ... that gas lighting inspired Stephen Gunzenhauser to start a classical music festival?
- ... that in 1994, Anthony Pople created two computer programs to analyse classical music?
- ... that WFMT classical music radio host Don Tait owned such a large collection of recordings that he had to buy a house and have its floor reinforced to accommodate the weight?
Selected image
-
Image 1Photo: Guillaume PiolleThe anatomy of a Périnet piston valve, this one taken from a B♭ trumpet. When depressed, the valve diverts the air stream through additional tubing, thus lengthening the instrument and lowering the harmonic series on which the instrument is vibrating (i.e., it lowers the pitch). Trumpets generally use three valves, with some variations, such as a piccolo trumpet, having four. When used singly or in combination, the valves make the instrument fully chromatic, or capable of playing all twelve pitches of classical music. Trumpets may also use rotary valves instead.
-
Image 2Painting: Thomas GainsboroughJohann Christian Bach (5 September 1735 – 1 January 1782) was a composer of the Classical era, the eighteenth child of Johann Sebastian Bach, and the youngest of his eleven sons. Bach was taught by his father and then, after the latter's death, by his half-brother C. P. E. Bach. Bach moved to Italy in 1754, and then to London in 1762, where he became known as the "London Bach". Bach's compositions include eleven operas, as well as chamber music, orchestral music and compositions for keyboard music. In 1764 Bach met Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, who was eight at the time, and spent five months teaching him composition. He had considerable influence on Mozart, and was later described by scholars as his "only, true teacher".
This portrait of Bach was painted in 1776 by Thomas Gainsborough, as part of a collection started by Bach's former teacher Padre Martini. It now hangs in the National Portrait Gallery, London. -
Image 3
 Ballet is a formalized form of dance with its origins in the French court, further developed in France and Russia as a concert dance form.
Ballet is a formalized form of dance with its origins in the French court, further developed in France and Russia as a concert dance form. -
Image 4Photograph credit: William P. Gottlieb; restored by Adam CuerdenBilly Strayhorn (November 29, 1915 – May 31, 1967) was an American jazz composer, pianist, lyricist, and arranger, best remembered for his long-time collaboration with bandleader and composer Duke Ellington that lasted nearly three decades. Though classical music was Strayhorn's first love, his ambition to become a classical composer went unrealized because of the harsh reality of a black man trying to make his way in the world of classical music, which at that time was almost completely white. He was introduced to the music of pianists like Art Tatum and Teddy Wilson at age 19, and the artistic influence of these musicians guided him into the realm of jazz, where he remained for the rest of his life. This photograph of Strayhorn was taken by William P. Gottlieb in the 1940s.
-
Image 5Photograph: David IliffThe Royal Albert Hall is a concert hall, seating a maximum of 5,272, on the northern edge of South Kensington, London. Constructed beginning in 1867, the hall was inaugurated on 29 March 1871. Since 1941 it has held The Proms, an eight-week summer season of daily orchestral classical music concerts and other events.
-
Image 6

A picture of the first theatre drawn shortly before it burned down in 1808.
The Royal Opera House is an opera house and major performing arts venue in the London district of Covent Garden. The large building, often referred to as simply "Covent Garden", is the home of The Royal Opera, The Royal Ballet and the Orchestra of the Royal Opera House. -
Image 7Photo: W. J. Mayer; Restoration: Lise BroerA bust of the German composer and pianist Ludwig van Beethoven (1770–1827), made from his death mask. He was a crucial figure in the transitional period between the Classical and Romantic eras in Western classical music, and remains one of the most acclaimed and influential composers of all time. Born in Bonn, of the Electorate of Cologne and a part of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation in present-day Germany, he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. His hearing began to deteriorate in the late 1790s, yet he continued to compose, conduct, and perform, even after becoming completely deaf.
-
Image 8Photograph credit: Eugène Pirou; restored by Adam CuerdenJules Massenet (12 May 1842 – 13 August 1912) was a French composer of the Romantic era, best known for his operas. Between 1867 and his death, he wrote more than forty stage works in a wide variety of styles, from opéra comique to grand depictions of classical myths, romantic comedies and lyric dramas, as well as oratorios, cantatas and ballets. Massenet had a good sense of the theatre and of what would succeed with the Parisian public. Despite some miscalculations, he produced a series of successes that made him the leading opera composer in France in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. By the time of his death, he was regarded as old-fashioned; his works, however, began to be favourably reassessed during the mid-20th century, and many have since been staged and recorded. This photograph of Massenet was taken by French photographer Eugène Pirou in 1875.
-
Image 9
 The Teatro alla Scala (or La Scala, as it is known), in Milan, Italy, is one of the world's most famous opera houses. The theatre was inaugurated on 3 August 1778, under the name Nuovo Regio Ducal Teatro alla Scala with Salieri's Europa riconosciuta.
The Teatro alla Scala (or La Scala, as it is known), in Milan, Italy, is one of the world's most famous opera houses. The theatre was inaugurated on 3 August 1778, under the name Nuovo Regio Ducal Teatro alla Scala with Salieri's Europa riconosciuta. -
Image 10
 Stradivarius is one of the violins, violas, cellos and other string instruments built by members of the Italian Stradivari family, particularly Antonio Stradivari.
Stradivarius is one of the violins, violas, cellos and other string instruments built by members of the Italian Stradivari family, particularly Antonio Stradivari. -
Image 11Sheet music for the Polonaise in A-flat major, Op. 53, a solo piano piece written by Frédéric Chopin in 1842. This work is one of Chopin's most admired compositions and has long been a favorite of the classical piano repertoire. The piece, which is very difficult, requires exceptional pianistic skills and great virtuosity to be interpreted. A typical performance of the polonaise lasts seven minutes.
Topics
Things you can do
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus

























































































