Chromosome 21 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Chromosome 21 is both the smallest human autosome and chromosome,[4] with 46.7 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) representing about 1.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Most people have two copies of chromosome 21, while those with three copies of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21) have Down syndrome.
| Chromosome 21 | |
|---|---|
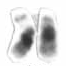 Human chromosome 21 pair after G-banding. One is from the mother, one is from the father. | |
 Chromosome 21 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 45,090,682 bp (CHM13) |
| No. of genes | 215 (CCDS)[1] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Acrocentric[2] (12.0 Mbp[3]) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 21 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 21 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 21 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 21 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000021 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000683 (FASTA) |
Researchers working on the Human Genome Project announced in May 2000 that they had determined the sequence of base pairs that make up this chromosome.[5] Chromosome 21 was the second human chromosome to be fully sequenced, after chromosome 22.
Genes
editNumber of genes
editThe following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 21. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation, their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project (CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. Thus CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.[6]
| Estimated by | Protein-coding genes | Non-coding RNA genes | Pseudogenes | Source | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDS | 212 | — | — | [1] | 2022-10-26 |
| HGNC | 215 | 193 | 194 | [7] | 2024-04-10 |
| Ensembl | 221 | 447 | 185 | [8] | 2023-07-17 |
| UniProt | 246 | — | — | [9] | 2024-10-02 |
| NCBI | 256 | 356 | 207 | [10][11][12] | 2017-05-19 |
Gene list
editThe following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 21. For complete list, see the link in the infobox at the top of the article.
- ABCG1: encoding ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 1
- ADAMTS1 encoding enzyme a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 1
- ADAMTS5: encoding enzyme a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 5
- ADARB1: encoding enzyme double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1
- AGPAT3: encoding enzyme 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase gamma
- AIRE: encoding protein autoimmune regulator
- APP: encoding amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein (peptidase nexin-II, Alzheimer disease)[13]
- ATP5PF: encoding enzyme subunit ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondrial
- ATP5PO: encoding enzyme subunit ATP synthase subunit O, mitochondrial
- B3GALT5: encoding enzyme beta-1,3-galactosyltransferase 5
- BACE2: encoding enzyme beta-secretase 2
- BACH1: encoding transcription factor transcription regulator protein BACH1
- BRWD1: encoding bromodomain and WD repeat-containing protein 1
- BTG3: encoding protein BTG3
- C21orf58: encoding uncharacterized protein C21orf58
- C21orf62: expressed in tissues of the brain and reproductive organs
- C21orf91: encoding protein EURL homolog
- CBR1: encoding enzyme carbonyl reductase [NADPH] 1
- CBR3: encoding enzyme carbonyl reductase [NADPH] 3
- CBS: encoding enzyme cystathionine-beta-synthase
- CCT8: encoding T-complex protein 1 subunit theta
- CFAP298: encoding cilia- and flagella-associated protein 298
- CHAF1B: encoding chromatin assembly factor 1 subunit B
- CHODL: encoding chondrolectin, a C-type lectin
- CLDN8: encoding protein claudin-8
- CLDN14: encoding protein claudin-14
- CLDN17: encoding protein claudin-17
- CLIC6: encoding chloride intracellular channel protein 6
- COL6A1: encoding alpha-1 chain of collagen VI
- COL6A2: encoding alpha-2 chain of collagen VI
- COL18A1: encoding alpha-1 chain of collagen XVIII
- CRYAA: encoding alpha-crystallin A chain
- CRYZL1: encoing protein crystallin zeta-like 1
- CSTB: encoding protein cystatin-B
- CXADR: encoding protein coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor
- CYYR1: encoding protein cysteine and tyrosine rich 1
- DIP2A: Disco-interacting protein 2 homolog A
- DNAJC28: encoding protein DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 28
- DNMT3L: encoding protein DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3-like
- DOP1B: encoding protein dopey family member 2
- DSCAM: encoding cell adhesion molecule DSCAM
- DYRK1A: dual specificity tyrosine-(Y)-phosphorylation regulated kinase 1A
- ERG: encoding protein transcriptional regulator ERG
- ERVH48-1: encoding protein suppressyn
- ETS2: encoding protein C-ets-2
- FAM3B: encoding protein family with sequence similarity 3 member B
- FRGCA: producing long non-coding RNA FOXM1-regulated, gastric cancer associated
- FTCD: encoding enzyme formimidoyltransferase-cyclodeaminase
- GABPA: encoding GA-binding protein alpha chain
- GART: encoding enzyme trifunctional purine biosynthetic protein adenosine-3
- GATD3A: encoding glutamine amidotransferase-like class 1 domain-containing protein 3A, mitochondrial
- GRIK1: encoding glutamate receptor ionotropic, kainate 1
- H2BC12L: encoding histone H2B type F-S
- HLCS: encoding enzyme holocarboxylase synthetase (biotin-(propionyl-Coenzyme A-carboxylase (ATP-hydrolysing)) ligase)
- HMGN1: encoding non-histone chromosomal protein HMG-14
- HSPA13: encoding heat shock 70 kDa protein 13
- ICOSLG: encoding protein ICOS ligand
- IFNAR1: encoding interferon alpha/beta receptor 1
- IFNAR2: encoding interferon alpha/beta receptor 2
- IFNGR2: encoding interferon gamma receptor 2
- IL10RB: encoding interleukin-10 receptor subunit beta
- ITGB2: encoding protein integrin beta-2
- ITSN1: encoding protein intersectin-1
- JAM2: encoding protein junctional adhesion molecule B
- KCNE1: encoding potassium voltage-gated channel, Isk-related family, member 1
- KCNE2: encoding potassium voltage-gated channel, Isk-related family, member 2
- KCNJ6: encoding G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 2
- KCNJ15: encoding ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 15
- LRRC3: encoding leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 3
- LSS: encoding enzyme lanosterol synthase
- LTN1: encoding enzyme E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase listerin
- MAP3K7CL: encoding MAP3K7 C-terminal-like protein
- MCM3AP: encoding germinal-center associated nuclear protein
- MIR155 producing microRNA miR-155
- MIR3648: producing microRNA 3648
- MIS18A: encoding protein Protein Mis18-alpha
- MORC3: encoding MORC family CW-type zinc finger protein 3
- MRAP: encoding melanocortin-2 receptor accessory protein
- MRPL39: encoding 39S ribosomal protein L39, mitochondrial
- MRPS6: encoding 28S ribosomal protein S6, mitochondrial
- MX1: encoding interferon-induced GTP-binding protein Mx1
- MX2: encoding interferon-induced GTP-binding protein Mx2
- N6AMT1: N-6 adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase 1
- NDUFV3: encoding NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein 3, mitochondrial
- NRIP1: nuclear receptor-interacting protein 1
- OLIG1: encoding oligodendrocyte transcription factor 1
- OLIG2: encoding oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2
- PAXBP1: encoding protein GC-rich sequence DNA-binding factor homolog
- PCBP3: encoding poly(rC)-binding protein 3
- PCNT: encoding protein centrosomal pericentrin
- PCP4: encoding calmodulin regulator protein PCP4
- PDE9A: encoding enzyme high affinity cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 9A
- PDXK: encoding enzyme Pyridoxal kinase
- PFKL: encoding enzyme ATP-dependent 6-phosphofructokinase, liver type
- PIGP: encoding phosphatidylinositol N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase subunit P
- PKNOX1: encoding homeobox protein PKNOX1
- POFUT2: encoding enzyme GDP-fucose protein O-fucosyltransferase 2
- PRDM15: encoding PR domain zinc finger protein 15
- PRMT2: encoding enzyme protein arginine N-methyltransferase 2
- PSMG1: encoding protein proteasome assembly chaperone 1
- PTTG1IP: encoding pituitary tumor-transforming gene 1 protein-interacting protein
- PWP2: encoding periodic tryptophan protein 2 homolog
- RBM11: encoding protein splicing regulator RBM11
- RCAN1: encoding protein calcipressin-1
- RIPK4: encoding enzyme receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 4
- RNR4: RNA, ribosomal 45S cluster 4
- RRP1: encoding protein ribosomal RNA processing protein 1 homolog A
- RRP1B: encoding protein ribosomal RNA processing 1 homolog B
- RSPH1: encoding protein radial spoke head 1 homolog
- RUNX1: encoding protein Runt-related transcription factor 1
- RWDD2B: encoding protein RWD domain-containing protein 2B
- S100B: encoding calcium binding protein
- SAMSN1: encoding SAM domain-containing protein SAMSN-1
- SH3BGR: encoding SH3 domain-binding glutamic acid-rich protein
- SIK1: encoding serine/threonine-protein kinase SIK1
- SIM2: encoding protein single-minded homolog 2
- SLC5A3: encoding protein sodium/myo-inositol cotransporter
- SLC19A1: encoding protein reduced folate transporter
- SLC37A1: encoding glucose-6-phosphate exchanger SLC37A1
- SMIM11: encoding small integral membrane protein 11
- SOD1: encoding enzyme superoxide dismutase 1, soluble (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 1 (adult))
- SON: encoding protein SON
- SPATC1L: encoding protein SPATC1L
- SUMO3: encoding protein small ubiquitin-related modifier 3
- SYNJ1: encoding protein synaptojanin-1
- TCP10L: encoding T-complex protein 10A homolog 1
- TFF1: encoding protein trefoil factor 1
- TFF2: encoding protein trefoil factor 2
- TFF3: encoding protein trefoil factor 3
- TIAM1: Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor TIAM1
- TMPRSS2: encoding enzyme transmembrane protease serine 2
- TMPRSS3: encoding enzyme transmembrane protease, serine 3
- TMPRSS15: encoding enteropeptidase
- TPTE: encoding protein putative tyrosine-protein phosphatase TPTE
- TRAPPC10: encoding protein Trafficking protein particle complex subunit 10
- TRPM2: encoding protein transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 2
- TTC3: encoding protein tetratricopeptide repeat domain 3
- U2AF1: encoding splicing factor U2AF 35 kDa subunit
- UBASH3A: encoding ubiquitin-associated and SH3 domain-containing protein A
- UBE2G2: encoding ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 G2
- UMODL1-AS1: producing long non-coding RNA
- USP16: encoding enzyme ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 16
- USP25: encoding enzyme ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 25
- WDR4: encoding tRNA (guanine-N(7)-)-methyltransferase non-catalytic subunit WDR4
- ZBTB21: encoding zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 21
In addition, the chromosome has many genes for keratin-associated protein, with symbols: KRTAP6-1, KRTAP6-2, KRTAP6-3, KRTAP7-1, KRTAP8-1, KRTAP10-1, KRTAP10-2, KRTAP10-3, KRTAP10-4, KRTAP10-5, KRTAP10-6, KRTAP10-7, KRTAP10-8, KRTAP10-9, KRTAP10-10, KRTAP10-11, KRTAP10-12, KRTAP11-1, KRTAP12-1, KRTAP12-1, KRTAP12-2, KRTAP12-3, KRTAP12-4, KRTAP13-1, KRTAP13-2, KRTAP13-3, KRTAP13-4, KRTAP15-1, KRTAP19-1, KRTAP19-2, KRTAP19-3, KRTAP19-4, KRTAP19-5, KRTAP19-6, KRTAP19-7, KRTAP19-8, KRTAP20-1, KRTAP20-2, KRTAP20-3, KRTAP20-4, KRTAP21-1, KRTAP21-2, KRTAP21-3, KRTAP22-1, KRTAP22-2, KRTAP23-1, KRTAP24-1, KRTAP25-1, KRTAP26-1, KRTAP27-1.
Diseases and disorders
editThe following diseases and disorders are some of those related to genes on chromosome 21:
- Acute myeloid leukemia
- Alzheimer's disease[13]
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Atrial fibrillation, familial
- Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1
- Basal ganglia calcification
- Bartsocas–Papas syndrome
- Bethlem myopathy
- Closed angle glaucoma
- Cataract
- CHAND syndrome
- Down syndrome
- Epilepsy
- Erondu–Cymet syndrome
- Ewing sarcoma
- Galloway Mowat syndrome
- Glucocorticoid deficiency
- Hepatitis B (susceptibility to)
- Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy
- Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
- Homocystinuria
- Hyperhomocysteinemia
- Hypotrichosis
- Immunodeficiency
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Intellectual developmental disorder
- Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome
- Keppen–Lubinsky syndrome
- Knobloch syndrome
- Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-1
- Majewski osteodysplastic primordial dwarfism type II (MOPD II, or MOPD2)
- Non-small cell lung carcinoma[14]
- Neurodevelopmental disorder
- Nonsyndromic deafness
- Parkinson disease
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Phosphofructokinase deficiency
- Primary ciliary dyskinesia
- Primary immunodeficiency
- Primitive neuroectodermal tumor
- Prostate cancer
- Romano–Ward syndrome
- Spastic quadriplegia
- Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy
- Unverricht–Lundborg disease, a form of progressive myoclonus epilepsy
- ZTTK syndrome
Chromosomal conditions
editThe following conditions are caused by changes in the structure or number of copies of chromosome 21:
- Cancers: Rearrangements (translocations) of genetic material between chromosome 21 and other chromosomes have been associated with several types of cancer. For example, acute lymphoblastic leukemia (a type of blood cancer most often diagnosed in childhood) has been associated with a translocation between chromosomes 12 and 21. Another form of leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, has been associated with a translocation between chromosomes 8 and 21.
- In a small percentage of cases, Down syndrome is caused by a rearrangement of chromosomal material between chromosome 21 and another chromosome. As a result, a person has the usual two copies of chromosome 21, plus extra material from chromosome 21 attached to another chromosome. These cases are called translocation Down syndrome. Researchers believe that extra copies of genes on chromosome 21 disrupt the course of normal development, causing the characteristic features of Down syndrome and the increased risk of medical problems associated with this disorder.
- Other changes in the number or structure of chromosome 21 can have a variety of effects, including intellectual disability, delayed development, and characteristic facial features. In some cases, the signs and symptoms are similar to those of Down syndrome. Changes to chromosome 21 include a missing segment of the chromosome in each cell (partial monosomy 21) and a circular structure called ring chromosome 21. A ring chromosome occurs when both ends of a broken chromosome are reunited.
- Duplication in amyloid precursor protein (APP) locus (duplicated segment varies in length but includes APP) on Chromosome 21 was found to cause early onset familial Alzheimer's disease in a French family set (Rovelet-Lecrux et al. 2005) and a Dutch family set.[13] Compared to Alzheimer's caused by missense mutations in APP, the frequency of the Alzheimer's caused by APP duplications is significant. All patients that have an extra copy of APP gene due to the locus duplication show Alzheimer's with severe cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
Cytogenetic band
edit| Chr. | Arm[19] | Band[20] | ISCN start[21] |
ISCN stop[21] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[22] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | p | 13 | 0 | 311 | 1 | 3,100,000 | gvar | |
| 21 | p | 12 | 311 | 683 | 3,100,001 | 7,000,000 | stalk | |
| 21 | p | 11.2 | 683 | 1056 | 7,000,001 | 10,900,000 | gvar | |
| 21 | p | 11.1 | 1056 | 1274 | 10,900,001 | 12,000,000 | acen | |
| 21 | q | 11.1 | 1274 | 1367 | 12,000,001 | 13,000,000 | acen | |
| 21 | q | 11.2 | 1367 | 1584 | 13,000,001 | 15,000,000 | gneg | |
| 21 | q | 21.1 | 1584 | 2019 | 15,000,001 | 22,600,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 21 | q | 21.2 | 2019 | 2144 | 22,600,001 | 25,500,000 | gneg | |
| 21 | q | 21.3 | 2144 | 2330 | 25,500,001 | 30,200,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 21 | q | 22.11 | 2330 | 2485 | 30,200,001 | 34,400,000 | gneg | |
| 21 | q | 22.12 | 2485 | 2610 | 34,400,001 | 36,400,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 21 | q | 22.13 | 2610 | 2703 | 36,400,001 | 38,300,000 | gneg | |
| 21 | q | 22.2 | 2703 | 2858 | 38,300,001 | 41,200,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 21 | q | 22.3 | 2858 | 3200 | 41,200,001 | 46,709,983 | gneg |
References
edit- ^ a b "Search results - 21[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("has ccds"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. CCDS Release 24 for Homo sapiens. 2022-10-26. Retrieved 2022-12-23.
- ^ Tom Strachan; Andrew Read (2 April 2010). Human Molecular Genetics. Garland Science. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-136-84407-2.
- ^ a b c Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ "Chromosome 21".
- ^ Hattori, M.; Fujiyama, A.; Taylor, T. D.; Watanabe, H.; Yada, T.; Park, H.-S.; Toyoda, A.; Ishii, K.; Totoki, Y.; Choi, D.-K.; Soeda, E.; Ohki, M.; Takagi, T.; Sakaki, Y.; Taudien, S.; Blechschmidt, K.; Polley, A.; Menzel, U.; Delabar, J.; Kumpf, K.; Lehmann, R.; Patterson, D.; Reichwald, K.; Rump, A.; Schillhabel, M.; Schudy, A.; Zimmermann, W.; Rosenthal, A.; Kudoh, J.; et al. (2000). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 21". Nature. 405 (6784): 311–319. Bibcode:2000Natur.405..311H. doi:10.1038/35012518. PMID 10830953.
- ^ Pertea M, Salzberg SL (2010). "Between a chicken and a grape: estimating the number of human genes". Genome Biol. 11 (5): 206. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-206. PMC 2898077. PMID 20441615.
- ^ "Statistics & download files". HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. 2024-04-10. Retrieved 2024-10-06.
- ^ "Chromosome 21: Chromosome summary - Homo sapiens". Ensembl Release 110. 2023-07-17. Retrieved 2024-02-17.
- ^ "Human chromosome 21: entries, gene names and cross-references to MIM". UniProt. 2024-10-02. Retrieved 2024-10-06.
- ^ "Search results - 21[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ^ "Search results - 21[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ( ("genetype miscrna"[Properties] OR "genetype ncrna"[Properties] OR "genetype rrna"[Properties] OR "genetype trna"[Properties] OR "genetype scrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snorna"[Properties]) NOT "genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ^ "Search results - 21[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype pseudo"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ^ a b c Sleegers K, Brouwers N, Gijselinck I, Theuns J, Goossens D, Wauters J, Del-Favero J, Cruts M, van Duijn CM, Van Broeckhoven C (2006). "APP duplication is sufficient to cause early onset Alzheimer's dementia with cerebral amyloid angiopathy". Brain. 129 (Pt 11): 2977–83. doi:10.1093/brain/awl203. PMID 16921174.
- ^ Kohno, T.; Kawanishi, M.; Matsuda, S.; Ichikawa, H.; Takada, M.; Ohki, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Yokota, J. (March 1998). "Homozygous deletion and frequent allelic loss of the 21q11.1-q21.1 region including the ANA gene in human lung carcinoma". Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer. 21 (3): 236–243. doi:10.1002/(sici)1098-2264(199803)21:3<236::aid-gcc8>3.0.co;2-0. ISSN 1045-2257. PMID 9523199. S2CID 24082301.
- ^ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. ISBN 978-3-318-02253-7.
- ^ Sethakulvichai, W.; Manitpornsut, S.; Wiboonrat, M.; Lilakiatsakun, W.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. (2012). "Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images". 2012 Ninth International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE). pp. 276–282. doi:10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965. ISBN 978-1-4673-1921-8. S2CID 16666470.
- ^ "p": Short arm; "q": Long arm.
- ^ For cytogenetic banding nomenclature, see article locus.
- ^ a b These values (ISCN start/stop) are based on the length of bands/ideograms from the ISCN book, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Arbitrary unit.
- ^ gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
- Antonarakis SE, Lyle R, Dermitzakis ET, Reymond A, Deutsch S (2004). "Chromosome 21 and down syndrome: from genomics to pathophysiology". Nat Rev Genet. 5 (10): 725–38. doi:10.1038/nrg1448. PMID 15510164. S2CID 5487794.
- Antonarakis SE, Lyle R, Deutsch S, Reymond A (2002). "Chromosome 21: a small land of fascinating disorders with unknown pathophysiology". Int J Dev Biol. 46 (1): 89–96. PMID 11902692.
- Antonarakis SE (2001). "Chromosome 21: from sequence to applications". Curr Opin Genet Dev. 11 (3): 241–6. doi:10.1016/S0959-437X(00)00185-4. PMID 11377958.
- Gilbert F (1997). "Disease genes and chromosomes: disease maps of the human genome. Chromosome 21". Genet Test. 1 (4): 301–6. doi:10.1089/gte.1997.1.301. PMID 10464663.
- Hattori M, Fujiyama A, Taylor TD, Watanabe H, Yada T, Park HS, Toyoda A, Ishii K, Totoki Y, Choi DK, Groner Y, Soeda E, Ohki M, Takagi T, Sakaki Y, Taudien S, Blechschmidt K, Polley A, Menzel U, Delabar J, Kumpf K, Lehmann R, Patterson D, Reichwald K, Rump A, Schillhabel M, Schudy A, Zimmermann W, Rosenthal A, Kudoh J, Schibuya K, Kawasaki K, Asakawa S, Shintani A, Sasaki T, Nagamine K, Mitsuyama S, Antonarakis SE, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Nordsiek G, Hornischer K, Brant P, Scharfe M, Schon O, Desario A, Reichelt J, Kauer G, Blocker H, Ramser J, Beck A, Klages S, Hennig S, Riesselmann L, Dagand E, Haaf T, Wehrmeyer S, Borzym K, Gardiner K, Nizetic D, Francis F, Lehrach H, Reinhardt R, Yaspo ML (2000). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 21". Nature. 405 (6784): 311–9. Bibcode:2000Natur.405..311H. doi:10.1038/35012518. PMID 10830953.
- Sawinska M, Ladon D (2004). "Mechanism, detection and clinical significance of the reciprocal translocation t(12;21)(p12;q22) in the children suffering from acute lymphoblastic leukaemia". Leuk Res. 28 (1): 35–42. doi:10.1016/S0145-2126(03)00160-7. PMID 14630078.
- Rovelet-Lecrux A, Hannequin D, Raux G, Le Meur N, Laquerriere A, Vital A, Dumanchin C, Feuillette S, Brice A, Vercelletto M, Dubas F, Frebourg T, Campion D (2005). "APP locus duplication causes autosomal dominant early-onset Alzheimer disease with cerebral amyloid angiopathy". Nature Genetics. 38 (1): 24–6. doi:10.1038/ng1718. PMID 16369530. S2CID 559054.
- Rauch, Anita; Thiel, Christian T.; Schindler, Detlev; Wick, Ursula; Crow, Yanick J.; Ekici, Arif B.; van Essen, Anthonie J.; Goecke, Timm O.; Al-Gazali, Lihadh; Chrzanowska, Krystyna H.; Zweier, Christiane; Brunner, Han G.; Becker, Kristin; Curry, Cynthia J.; Dallapiccola, Bruno; Koenraad Devriendt; Arnd Dörfler; Esther Kinning; André Megarbane; Peter Meinecke; Robert K. Semple; Stephanie Spranger; Annick Toutain; Richard C. Trembath; Egbert Voss; Louise Wilson; Raoul Hennekam; Francis de Zegher; Helmut-Günther Dörr; André Reis (2008). "Mutations in the Pericentrin (PCNT) Gene Cause Primordial Dwarfism". Science Online. 319 (5864): 816–9. Bibcode:2008Sci...319..816R. doi:10.1126/science.1151174. PMID 18174396. S2CID 23055733.
External links
edit- National Institutes of Health. "Chromosome 21". Genetics Home Reference. Archived from the original on 2011-06-05. Retrieved 2017-05-06.
- "Chromosome 21". Human Genome Project Information Archive 1990–2003. Retrieved 2017-05-06.